Saturday, April 12, 2014
biogeographic maps
http://www.planetaryvisions.com/Project.php?pid=2218
A biogeographic map is a thematic map that displays the distribution of species. This map is used to determine what organisms are where and what factors, geographically contribute to this. An example of this can be seen above in this graph displaying vegetation and regions. This is important for understanding where species are and migration patterns.
standardized choropleth map
http://www.directionsmag.com/articles/choropleth-mapping-with-exploratory-data-analysis/123579
In order to account for different sized land masses, the standardized map used aerially averaged data instead of the total value. this allows every sized unit to be compared to each other. An example of this can be seen in the above map of the population density. This is a better mapping technique of all choropleth maps because it allows for the comparison of different unit sizes. This map shows the population of different sized areas and shades them according to the quantile it falls into. Each area can now be compared to each other.
In order to account for different sized land masses, the standardized map used aerially averaged data instead of the total value. this allows every sized unit to be compared to each other. An example of this can be seen in the above map of the population density. This is a better mapping technique of all choropleth maps because it allows for the comparison of different unit sizes. This map shows the population of different sized areas and shades them according to the quantile it falls into. Each area can now be compared to each other.
climograph
http://www.colorado.edu/geography/extra/geogweb/bouldercreek-2/preview/page2.html
A climographs display climate information such as precipitation or monthly average temperatures etc. This graph allows users to see the change in the measured variable throughout the year. An example of this can be seen above in the climograph of Boulder, Colorado. The graph shows the average precipitation and monthly temperatures for the year. this map is used to determine why flash floods occur in Boulder.
population profile
http://www.census.gov/2010census/
A population profile is a chart graphing all the distribution of the population according to their ages. An example of this can be seen above in the chart where the population is represented by their sex and age. This is an application used by the census to demonstrate the demographics of age group and sex in proportion to the total population.
Index value plot
http://wattsupwiththat.com/2011/12/09/the-november-amo-index-goes-negative-first-time-since-1996/
An index value plots data on a line graph as index values instead of absolute values. A point of reference is also displayed and used to compare the data. An example of this can be seen above. This a line graph plotting the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation index. The point of reference allows the comparison to be made of when the values are negative (below the reference point) and when they are positive(above the reference).
An index value plots data on a line graph as index values instead of absolute values. A point of reference is also displayed and used to compare the data. An example of this can be seen above. This a line graph plotting the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation index. The point of reference allows the comparison to be made of when the values are negative (below the reference point) and when they are positive(above the reference).
Friday, April 11, 2014
Lorenz graph
http://www.rba.gov.au/publications/bulletin/2012/mar/3.html
A Lorenz graph displays a cumulative distribution function. It shows the proportions of a wealth distribution developed by Lorenz in 1905. It is mostly used in an economic application. The equality line is graphed as X=Y. The curve is the actual data graphed of the wealth distribution. This can be seen in the map above. The actual wealth and income fall below the equal distribution line. The percentages of each wealth or income and households can be found on the x and y axis.
A Lorenz graph displays a cumulative distribution function. It shows the proportions of a wealth distribution developed by Lorenz in 1905. It is mostly used in an economic application. The equality line is graphed as X=Y. The curve is the actual data graphed of the wealth distribution. This can be seen in the map above. The actual wealth and income fall below the equal distribution line. The percentages of each wealth or income and households can be found on the x and y axis.
Bilateral graph
http://seekingalpha.com/article/241440-will-octobers-improved-trade-deficit-continue
A bilateral graph displays two related sets of variables/data through a bar graph, a histogram, a line graph etc. It make sit easier to see and observe more than one set of data at one time. An example of this can be seen above. This graph is a line graph displaying the US trade deficit for each month for the year 2009 and 2010. By using a bilateral line graph, the two sets of data can be compared and trends can be noticed.
A bilateral graph displays two related sets of variables/data through a bar graph, a histogram, a line graph etc. It make sit easier to see and observe more than one set of data at one time. An example of this can be seen above. This graph is a line graph displaying the US trade deficit for each month for the year 2009 and 2010. By using a bilateral line graph, the two sets of data can be compared and trends can be noticed.
Nominal area choropleth map
https://courseware.e-education.psu.edu/courses/geog482/policies.shtml
A nominal area choropleth map displays aerial data through the use of colors or patterns to define different areas or regions. The variable mapped is nominal and not ranked. An example of this can be seen in the map above. The variable being mapped are minority groups with the highest percentage of state population and each group is assigned a color.
Unstandardized Choropleth Map
An unstandardized Choropleth Map is a thematic choropleth that uses the original data instead of the average. An example of this can be seen above. This map is classified using the original data and is broken up into one fifth of the population in each class.
Bivariate choropleth map
http://www.geo.unizh.ch/~annal/Choropleth%20maps.html
A bivariate choropleth map displays two variables one map, simultaneously. This is done by using two different symbols or colors/shading for each variable. This map makes it easier to observe a geographical relationship between two variables. An example of this can be seen in the map above. The two variables are the percentage of the population under 18, in red, and the percentage of rural population, in blue. By mapping them into one map, the places where they overlap are easier to observe and a relationship can be determined, if there is one. The relationship is shown by the bottom left chart.
A bivariate choropleth map displays two variables one map, simultaneously. This is done by using two different symbols or colors/shading for each variable. This map makes it easier to observe a geographical relationship between two variables. An example of this can be seen in the map above. The two variables are the percentage of the population under 18, in red, and the percentage of rural population, in blue. By mapping them into one map, the places where they overlap are easier to observe and a relationship can be determined, if there is one. The relationship is shown by the bottom left chart.
Monday, April 7, 2014
Parallel coordinate graph
http://vis.lbl.gov/Vignettes/Incite7/
A parallel coordinate graph helps to organize and visualize multiple variables. Equally spaced parallel axis are placed and lines connect at each axis(nth coordinate) depending on their ith value. An example of this can be seen above in this plot of beam revolution. the parallel coordinates help to demonstrate when the beam particles are injected into the simulation by using these coordinates.
A parallel coordinate graph helps to organize and visualize multiple variables. Equally spaced parallel axis are placed and lines connect at each axis(nth coordinate) depending on their ith value. An example of this can be seen above in this plot of beam revolution. the parallel coordinates help to demonstrate when the beam particles are injected into the simulation by using these coordinates.
Similarity Matrix
http://spie.org/x48704.xml?pf=true&ArticleID=x48704
A similarity matrix contains data sets or points and represent the similarity between these data sets. Each element contains a measure of similarity. In the matrix above, the burgundy diagonal shows the most similarly between the drug reponses. The blue elements had less in common.
A similarity matrix contains data sets or points and represent the similarity between these data sets. Each element contains a measure of similarity. In the matrix above, the burgundy diagonal shows the most similarly between the drug reponses. The blue elements had less in common.
Triangular plot
http://www.dplot.com/triangle-plot.htm
A triangular plot graphs three variables, one each side. Any three variables plotted sum up to one and are independent of each. An example of this can be see above. This triangular plot is used for geotechnical applications for classifying soils. The three variables plotted are different soil cassifications. A soil can be classified by just knowing the percentage of two variables. They are independent of each other.
A triangular plot graphs three variables, one each side. Any three variables plotted sum up to one and are independent of each. An example of this can be see above. This triangular plot is used for geotechnical applications for classifying soils. The three variables plotted are different soil cassifications. A soil can be classified by just knowing the percentage of two variables. They are independent of each other.
Unclassed choropleth maps
http://www.agroatlas.ru/en/content/climatic_maps/S_Temperature/S_Temperature_01/
An unclassed choropleth is a similar to a classed choropleth, but it does not have a set number of colors. Many different shadings of colors are used to depict the variable being mapped. It is a thematic map. An example of this is seen in the map above which maps the mean annual air temperatures for different portions of the earth. All the different shades are represented and defined in the scale on the bottom of the map.
An unclassed choropleth is a similar to a classed choropleth, but it does not have a set number of colors. Many different shadings of colors are used to depict the variable being mapped. It is a thematic map. An example of this is seen in the map above which maps the mean annual air temperatures for different portions of the earth. All the different shades are represented and defined in the scale on the bottom of the map.
Range graded proportional circle map
https://www.e-education.psu.edu/geog160/c3_p14.html
A range graded proportional circle map uses a set of circles that represent a certain amount and include a legend. These circles measure a variable and are proportionate to the value measured, unlike continuously graded proportional circle maps that use a scale. An example of this can be seen above in this map depicting unemployment in the US in the year 2000. Each circle represents a range and only five different sized circles will be found on the map.
A range graded proportional circle map uses a set of circles that represent a certain amount and include a legend. These circles measure a variable and are proportionate to the value measured, unlike continuously graded proportional circle maps that use a scale. An example of this can be seen above in this map depicting unemployment in the US in the year 2000. Each circle represents a range and only five different sized circles will be found on the map.
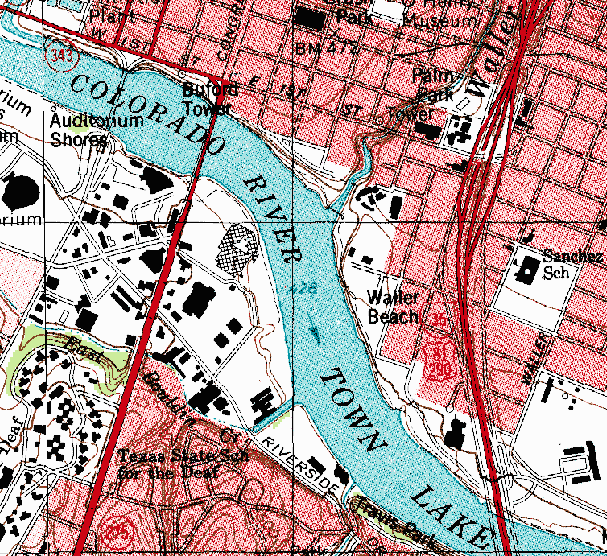
Continuously variable proportional circle map
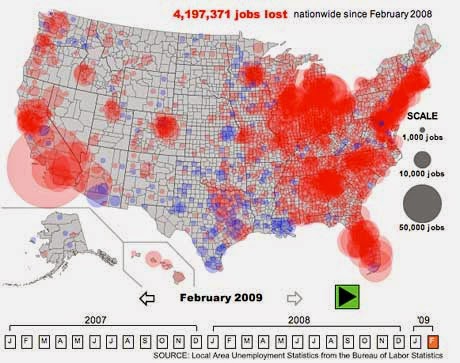
http://www.theguardian.com/news/datablog/2009/apr/13/week
A Continuously variable proportional circle map is a map that uses circles to represent data. These circles vary in size depending the the proportion of the variable being measured for the land area. An example of this can be seen above in this Continuously variable proportional circle map. This map shows the unemployment over all of the US. The large circles over the southern portion of California demonstrates that there is a large number of people unemployed in that region of California.
DLG
A DLG, digital line graph, is a cartographic map of of vectors that are digital representations of cartographic information. These graphs are derived from USGS quadrangle topographic maps. An example of this is seen above. This map contains lines (vectors) that contains different information.
DRG
A DRG (digital Raster graphic) is a scanned digital image of a USGS survey topographic map. It is done for computer use. They are normally used in GIS applications. An example of this can be seen above. This is a portion of a DRG of Texas. This can be used in GIS software as a layer because it is georeferenced to the Earth's surface.
Sunday, April 6, 2014
Isopachs
http://www.southampton.ac.uk/~imw/Durlston-Bay-Lower-Purbeck.htm
An isopach is a map that uses contour lines to represent a stratum or a group of strata that share the same thickness. An example of this is seen in the map above which shows the total Purbeck formation and the thickness is measured in feet. The isolines connect the points sharing similar thickness values.
An isopach is a map that uses contour lines to represent a stratum or a group of strata that share the same thickness. An example of this is seen in the map above which shows the total Purbeck formation and the thickness is measured in feet. The isolines connect the points sharing similar thickness values.
Isohyets
An isohyets is a line on a map that connects points that have the same amount of rainfall in a
given time period. An example of this is in the map above. This is an image of a map the amount of rainfall recorded by the Hong Kong Observatory from the 25-30th of August in 2004. Each line connects the points representing locations with the same amount of rainfall in the given period.
Isotachs
An isotach is a line on the weather map that connects points with similar recorded wind speeds. An example of this can be seen above in this weather map of the US. This map gives the temperatures and wind speeds taken on April 10, 2009. The wind speeds lines, isotachs, are labeled to show the values of all the points on the line.
Isobar Map
An isobar is a line on a map that connects points that have the same atmospheric pressure at a given time or over an average time period. An example of this is in the map above. This is an image of a weather map on the weather channel. The lines circling the L (low pressure) and the H (high pressure) are isobars and the points along the lines all correspond to the same pressure.
black and white aerial photography

Black and white aerial photography is an aerial photo that captures the same wavelength as the human eye, visible light. it is great for showing roads, shorelines, parcels and obvious details but not as detailed as the infrared aerial photos. Above is a black and white aerial taken in 1937 of Salt Lake City. This image was taking to show the urbanization that has occurred in the last years since the earlier aerial photograph.
Infrared aerial photo
http://geography.wr.usgs.gov/science/sacWetlands.html
Infrared aerial photography are pictures taken using devices that capture the infrared radiation given off by the earth's surface or other objects. These pictures are usually large land areas and can help show the changes in the land over time. Above is an infrared aerial photo of a wetland in Sacramento on the USGS website. Each color in the photograph represents the land.For example red shades represent more live vegetation and blue shades are dead vegetation or high in moisture land. This is shown here in the wetland photo.
Infrared aerial photography are pictures taken using devices that capture the infrared radiation given off by the earth's surface or other objects. These pictures are usually large land areas and can help show the changes in the land over time. Above is an infrared aerial photo of a wetland in Sacramento on the USGS website. Each color in the photograph represents the land.For example red shades represent more live vegetation and blue shades are dead vegetation or high in moisture land. This is shown here in the wetland photo.
Cartogram
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cartogram-2008_Electoral_Vote.gif
A cartogram is a map that organizes statistical information. A variable is chosen and is represented through land area and colors to represent a type of data. Above is an example of a cartogram and the variable being represented is the 2008 electoral projected votes. Each candidate is defined with a color and the areas shaded that color portray the majority vote in that area. This map uses land area to portray the projected voting for that area.
A cartogram is a map that organizes statistical information. A variable is chosen and is represented through land area and colors to represent a type of data. Above is an example of a cartogram and the variable being represented is the 2008 electoral projected votes. Each candidate is defined with a color and the areas shaded that color portray the majority vote in that area. This map uses land area to portray the projected voting for that area.
Saturday, March 22, 2014
Statistical Maps
http://www.census.gov/population/www/cen2000/maps/respop.html
A Statistical
Map is a type of map that shows the variation in quantity of a factor in the
area or geographic location. Three main types include a choropleth map,
proportional symbol maps, and to map. These maps make it easier to relate info
to a certain location. An example of this is the map above. It shows the
resident population for each state in the U.S. in the year 2000 from the census.
This is shown with shading of greens with a legend to define the interval for
each shade.
Doppler Radar
http://www.srh.noaa.gov/tlh/?n=event-20110327-hailstorms
Doppler Radar is a specialized radar system that uses the
Doppler effect as a tracking system to determine the location and velocity of
clouds, storms, precipitation, and more. It shows change over a span of time.
An example of this is shown above. This example shows a Doppler radar image of
Miller county, GA moments before 1.75 inch hail was produced. The legend on the
edge shows the intensity which is defined by the colors.
Correlation Matrix
http://yin.che.wisc.edu/images.htm
A correlation matrix is a matrix between all pairs of data
sets. An example of this is shown above. This is a correlation matrix of phage
T7 proteins. The behaviors are shown from high displayed in red, to low
displayed in blue. The red blocks that form a triangular shape are shown to be
highly correlated because they are involved in phase assembly process.
Star Plots
A star plot allows the viewer to compare multiple variables.
Each star represents a single observation. An example of this is shown above
and shows a star plot of automobile data. Each star represents a car model, and
each ray represents a variable and is proportional to that variables value.
Scatter Plot
http://onlinestatbook.com/chapter4/intro.html
A scatter plot is a graph that plots two values along two
axes. The scatter pattern demonstrates the correlation between the two
variables. A trend line demonstrates what the general pattern is. An example of
this is the chart above which displays the wife’s age versus husband’s age. The
dots represent each value and the graph shows a strong positive correlation
between the two values.
Histogram
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histogram
A histogram is a map of distribution of data. It represents
the frequency of a specific event happening. An example of this is shown above where the heights of black
cherry trees are plotted on the histogram. It is seen that 10 trees were found
to have a height of 80 feet.
Windrose Maps
A windrose is a symbol that shows the direction and wind
speed in a particular location. This is mostly used by meteorologists. This is
an example of a windrose of Raleigh-Durham from 1948 to 2013. The legend
demonstrates the colors designated to each speed and the slices demonstrate the
direction that can be found using the coordinate system. So most of the wind
was found to be in the SW direction with and average speed if 7.12 mph.
LIDAR
LIDAR , light detection and ranging, is used to create high
resolution maps. It is a remote sensing method that uses light as a laser to
detect varying physical features. This is an example of a LIDAR map of the
Interstate 510 Bridge in New Orleans taken in 2012. This uses the light lasers
to map this area and will be used to detect any flooding in urban areas
impacted by Hurricane Isaac.
DOQQ
http://lacoast.gov/maps/2005doqq/
DOQQ are aerial photographs or satellite imagery that are
digital. Each quarter covers one of a quadrangle. They are corrected to line up
with longitude and latitude lines. This is done due to the relief and the
camera angle. This map is an
example of DOQQ imagery of Louisiana after Hurricane Katrina and Rita in 2005.
This map is provided by USGS and was used to show the damage and to gain more
assistance in hurricane recovery.
Box Plot
http://nelsontouchconsulting.wordpress.com/2011/01/07/behold-the-box-plot/
A box plot is used most for displaying statistical
information and comparing data. It is made up of box and whiskers. Measurements
of the average, maximum, minimum and the average dispersion are things shown on
a box plot. This is an example of boxplots and it demonstrates the market for
Engineer compared to Market Base salary. Boxplots help in determining the range
of the data and compare it another set of data and see where it falls within
those values.
Stem and leaf plot
http://mainland.cctt.org/mathsummer/josephbond/stemandplots/stem-and-leaf_std.htm
A stem leaf plot organizes a set of numbers or data to make
it easier to read or understand.
The digits in the greatest place value are plotted in the left column
(stem) and the digits in the next greatest value is the plotted in the right
column know as the leaf. This is an example of a stem and leaf plot demonstrating
infant mortality rate in western Africa. The greatest place values are placed
in the stem column and the lowest is placed in the leaf column.
Proportional circle map
http://geographyfieldwork.com/DataPresentationMappingTechniques.htm
A proportional circle map shows values using a circle as a
symbol. The area of the circle is in proportion to the size of the value being
shown. This is an example of a proportional circle map. It was taken of Czech
Republic and displays the common languages with different sized circles and
colors. Each slice represents the proportion of those that speak that language.
Isopleth Map
http://geographyfieldwork.com/DataPresentationMappingTechniques.htm
Similar to an isoline, an isopleths is a continuous line
connecting two points of the same value together, representing a third dimension.
This map is an example of an isopleths map and shows gradual change over space.
This map demonstrates the precipitation on the 10th of June in 200.
Each value is represented by a different shading of blue and delineated using
isopleths or isolines.
propaganda map
http://www.learnnc.org/lp/editions/mapping/6434
A propaganda map is a map created with the goal to help a
certain cause and persuade the users to think or see something a certain way.
This map is an example of a propaganda map and was made during the cold war. This
map is a displays the USSR as being larger than Africa which gave the
perception of the USSR taking over Europe and having their armies spreading all
over Europe. This was done with the intentions to make users of the map to
support an increase in military spending.
DEM
http://www.satimagingcorp.com/svc/dem.html
Digital Elevation model displays an image of regularly
spaced grid of elevation points. It uses a three dimensional geodetic system
with the x-axis as easting’s, y axis as northing’s and z axis is the
elevation. This is an example of a
DEM and displays an image of Eritrea Africa. This is an IKONOS image, which
means the data, is from IKONOS satellite sensors.
Flow maps
http://euclid.psych.yorku.ca/SCS/Gallery/milestone/Test/thumb5/popup/bssn1_popup1-29.htm
Flow maps show the movement and
path of objects from one location to another. This map shows transit routes of
pedestrians through shaded lines and the density is demonstrated by the
thickness of the line. This is one of the first published flow maps made.
Dot distribution Map
http://lewishistoricalsociety.com/wiki2011/tiki-read_article.php?articleId=6
Dot Distribution maps shows the location of a certain type
of feature by using a dots as a symbol. The scatter pattern of the dots
demonstrates the spatial distribution of the feature. This map is of cell phone
tower locations in the US. It can be seen that there is more concentration of
cell phone towers in the east then in the west side of the US.
PLSS
http://www.co.pacific.wa.us/gis/desktopgis/web/index.html
Public land surveying system is a rectangular surveying
system mapping method, which is used to identify land, parcels before townships
and ranges are identified. It divides areas into townships and ranges. This is
an example of a PLSS map of Pacific county in Washington. The townships are
labeled on the vertical axis and the ranges are located on the horizontal axis.
Cadastral Map
http://www.gpem.uq.edu.au/graphic-presentation-maps
Cadastral
maps show the boundaries of land parcels in an area. It usually includes
details of who owns what and the actual description of the boundaries as well
as the parcel id. This map is a cadastral map of Montgomery County taken in
2010. It shows the boundaries of each parcel as well as information.
Mental Map
http://ocw.mit.edu/ans7870/MAS/MAS.965/f04/assignments/tripti/Assignment10/index.htm
A mental map is a map made of one’s own perception and
knowledge of an area that they have interacted with. Nothing is to scale and
the map of the same area made by another person may look completely different. This
map is drawn from the perspective of Francis of Cambridge, Boston. It shows his
perception of where different landmarks and places are and uses his own
symbolism to represent each place.
Tuesday, March 11, 2014
Univariate Choropleth Map
http://visualizingeconomics.com/blog/2007/08/11/united-states-poverty-map
This map is an example of an univariate choropleth map. This map shows one type of data set value and uses different shading from yellow to red to show the concentration. This map plots the income in % of the United states. This map specifically shows the % living in poverty.
This map is an example of an univariate choropleth map. This map shows one type of data set value and uses different shading from yellow to red to show the concentration. This map plots the income in % of the United states. This map specifically shows the % living in poverty.
Thursday, February 27, 2014
KML Google earth
The type of remote sensing data shown is the fire activity
detected by MODIS satellite. This is demonstrated through the use of circles
with varying colors to determine the time interval of the fire detection; Red
being most recent and yellow being the longer interval of detection. Applications
can be anywhere firefighters to researchers wanting to know what locations are
more prone to fire activity. The image itself does not give too much detail and
does not have good resolution. In google earth, the resolution changes as you
zoom into a location and the circle becomes a defined area which is helpful for
pinpointing the exact location of the incident. This information is relevant to
the management of fires and is made into Keyhole Markup Language (KML/KMZ) format
for use in Google Earth and other virtual globe applications. Geospatial data
are organized by different geographic regions. They include the location and
characterization of the type of detection including size and their significance
in the U.S.
Wednesday, February 26, 2014
Orienteering map
This map shows a orienteering map and is designed to be used
for orienteering competitions. It uses a topographic map with additional
details included for the use of the competitor to be able to navigate through
the different areas. Land features
represented by symbols and can be interpreted in any language. These symbols
are defined by a legend in the bottom left. Contour lines are used to demonstrate
the terrain, and symbols and features include the forest density, water
features as well as roads and buildings. A scale is labeled on the top and uses
a ratio format. The base maps are usually LIDAR maps. Generalization is used
for these maps to include necessary details and to avoid confusion.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)